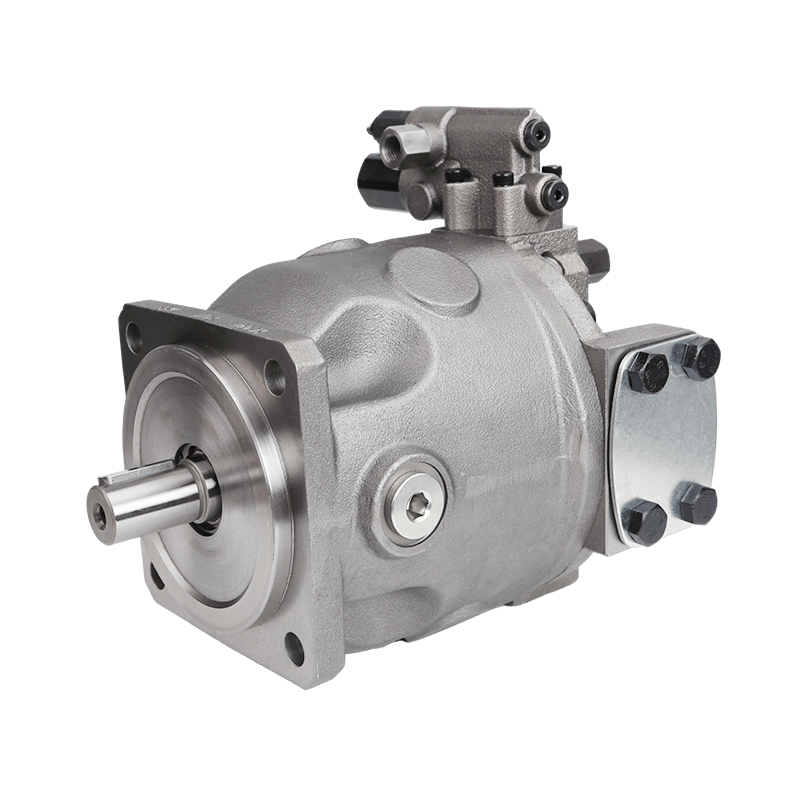
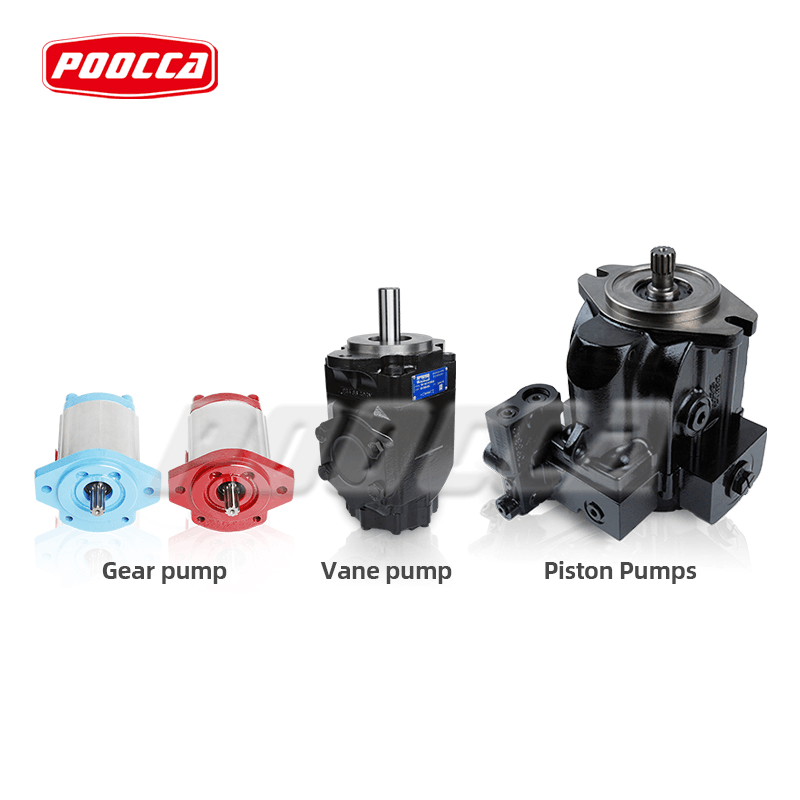
Hydraulic pumps serve as the cornerstone of industrial machinery, transforming mechanical energy into hydraulic energy to drive a diverse array of operations. From construction equipment to manufacturing lines, selecting the appropriate hydraulic pump ensures optimal performance, longevity, and cost efficiency. This guide explores the essential considerations for choosing the right hydraulic pump, including types, operational demands, efficiency metrics, installation practices, and manufacturer selection. By evaluating these factors systematically, industrial operations can achieve reliable power transmission and minimize downtime.

Understanding Hydraulic Pump Types
Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical power into fluid energy, making them indispensable in systems requiring precise control and high force output. The three primary categories—gear, vane, and piston pumps—each offer distinct advantages tailored to specific industrial scenarios.
Gear Pumps: Basics and Applications
Gear pumps operate through the meshing of two or more gears to trap and displace fluid, delivering consistent flow in simpler setups. Their straightforward design contributes to robustness, particularly in environments with moderate demands.
Efficiency and cost-effectiveness define gear pumps’ appeal, with mechanical efficiencies typically ranging from 70% to 75%. Initial investment remains low, positioning them as economical choices for budget-conscious applications. Operating speeds span 1200 to 3600 RPM, influencing flow consistency, while lifespan hinges on gear material and fluid quality, often extending through routine lubrication.
In practice, gear pumps excel in automotive assembly lines for lubrication circuits and low-pressure fluid transfer in material handling equipment. Their tolerance for contaminated fluids further suits them for rugged industrial floors where filtration challenges persist.
Vane Pumps: Working Principle and Suitability
Vane pumps employ sliding vanes within a rotor to create expanding and contracting chambers, enabling variable displacement and smoother flow than fixed-volume alternatives. This mechanism suits medium-pressure systems where adaptability matters.
Achieving up to 85% mechanical efficiency, vane pumps support power outputs up to 75 kW, balancing performance with energy savings. Compact footprints reduce space requirements in tight machinery enclosures, though complexity elevates costs over gear models. High-grade metals enhance durability, resisting wear in continuous operations.
Fluid viscosity poses a limitation, as thicker media can strain the vanes, potentially dropping efficiency. Applications thrive in injection molding machines and printing presses, where precise, pulsation-free delivery maintains product quality.
Piston Pumps: Advantages and Limitations
Piston pumps utilize reciprocating pistons in cylinders to generate high pressures, offering versatility through axial, radial, or bent-axis configurations. Their design excels in demanding environments needing exact flow regulation.
With efficiencies reaching 90%, piston pumps minimize energy loss, supporting variable displacement for load-responsive operation. Elevated upfront costs reflect premium construction, yet extended lifespans offset expenses in high-cycle use. Speeds of 600 to 1800 RPM promote longevity by curbing heat buildup.
Heavy machinery like hydraulic presses and excavators leverage piston pumps for their pressure-handling prowess up to 5000 psi. Drawbacks include sensitivity to contamination, necessitating superior filtration to prevent scoring.
Selecting among these types demands alignment with pressure profiles, flow needs, and environmental factors, as detailed in manufacturer datasheets for informed decisions.
Assessing Industrial Requirements

Tailoring hydraulic pumps to industrial contexts begins with a thorough audit of system parameters. Pressure ratings, flow dynamics, and fluid properties dictate compatibility, ensuring seamless integration and sustained output.
Analyzing Operational Pressure Needs
Pressure capacity forms the bedrock of pump selection, as under-specced units risk failure under load, while overcapacity invites inefficiency. Industrial systems routinely span 1000 to 5000 psi, with peaks in forging or mining applications demanding reinforcements.
Robust designs for elevated pressures incorporate reinforced housings, inflating costs by 20% or more compared to low-pressure variants. High-grade alloys withstand cyclic stresses, prolonging service intervals. For a 3000 psi conveyor drive, matching pump ratings averts cavitation and secures throughput.
Flow Rate Considerations for Efficiency
Flow rate governs actuator speed and system responsiveness, measured in gallons per minute (GPM). Undersized flows delay cycles, eroding productivity, whereas excess generates heat and hikes energy bills.
Calculations factor actuator volumes, cycle times, and safety margins; a 15 GPM demand at 2500 psi contrasts sharply with 30 GPM counterparts, influencing pump displacement. Size-speed interplay modulates output—larger bores yield higher volumes but escalate power draws. Optimizing this nexus curbs operational overheads in assembly automation.
Evaluating Fluid Compatibility
Hydraulic fluids vary from mineral oils to synthetics, each interacting uniquely with pump internals. Phosphate esters, common in fire-prone settings, necessitate corrosion-resistant coatings to avert degradation.
Viscosity-temperature interplay affects slippage; low temperatures thicken fluids, spiking torque needs, while heat thins them, risking leaks. Incompatible pairings accelerate seal erosion, curtailing lifespan by 30%. Compatibility charts guide selections, preserving efficiency in chemical processing plants.
Performance and Efficiency Factors
Efficiency metrics illuminate a pump’s true value, encompassing volumetric, mechanical, and holistic yields. Size, speed, temperature, and viscosity interplay to shape real-world viability.
Hydraulic Pump Efficiency Metrics
Mechanical efficiency tracks power conversion from shaft to fluid, averaging 75-85% across models. Volumetric efficiency, gauging slip-free displacement, peaks at 95% in premium units, curbing internal recirculation losses.
Overall efficiency merges these, targeting 80%+ to slash fuel consumption in mobile hydraulics. High performers reduce carbon footprints, aligning with sustainability mandates in modern factories.
Impact of Pump Size and Speed on Performance
Displacement size dictates per-revolution volume, with larger variants boosting GPM at the expense of torque. Speed amplifies this but accelerates wear via friction, shortening intervals in high-RPM scenarios.
Equilibrium favors application-specific tuning; oversized pumps in low-demand setups waste energy, while undersized ones overheat. Simulation software aids in plotting curves for balanced profiles in conveyor systems.
Temperature and Viscosity Effects on Pump Operation
Optimal viscosity (around 30-100 cSt) lubricates clearances, averting metal-to-metal contact. Extremes—sub-zero thickening or heat-induced thinning—impair sealing, dropping efficiency by 10-20%.
Thermal management via coolers or heaters stabilizes conditions, vital in foundries where ambient swings challenge consistency. Monitoring sensors enable predictive adjustments, forestalling failures.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Beyond selection, execution and upkeep determine return on investment. Proper protocols extend asset life, curbing unplanned halts.
Installation Best Practices for Longevity
Precision alignment between pump and prime mover mitigates vibration, with tolerances under 0.005 inches preserving seals. Clean, temperate environs shield against ingress, while post-install flow-pressure verifications confirm baselines.
Mounting on damped bases absorbs shocks in vibrating setups, enhancing joint integrity.
Routine Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Scheduled oil changes every 1000 hours flush contaminants, while inspections flag anomalies like cavitation whines or pressure dips. Filtration at 10 microns sustains cleanliness, slashing wear rates.
Prompt interventions—flushing for overheating or vane adjustments for slippage—avert escalations, maintaining 99% uptime in critical paths.
Replacement Strategies and Cost Management
Life-cycle analyses weigh acquisition against downtime and repairs; a mid-tier pump’s total ownership might undercut premium tags via lower service needs. Stocking spares like seals streamlines responses.
Phased upgrades to efficient models recoup via 15% energy savings, timed with obsolescence cycles.
Selecting the Right Manufacturer and Model
Manufacturer vetting ensures quality bedrock, with model comparisons honing fit. Reputation, range, and support form the triad.
Criteria for Choosing Hydraulic Pump Manufacturers
Established players boast proven track records, evidenced by ISO certifications and global footprints. Broad portfolios signal versatility, accommodating evolutions like electrification hybrids.
Customization prowess—altering displacements or mounts—tailors to niches, while R&D investments yield innovations like low-noise variants.
Comparing Different Models for Specific Use Cases
Efficiency ratings spotlight leaders; a 90% model trims bills over 80% peers despite premiums. Specs like max pressure (5000 psi) and GPM (50+) must sync with loads, with materials like hardened steel suiting abrasives.
Build scrutiny reveals forged housings’ edge in fatigue resistance.
Warranty and Support Services Evaluation
Extended warranties (12-24 months) underscore confidence, covering defects comprehensively. Responsive support—remote diagnostics, field techs—minimizes disruptions, with parts availability under 48 hours ideal.
After-sales ecosystems, including training, fortify user competencies.
In conclusion, hydraulic pump selection weaves technical acumen with strategic foresight, yielding systems that propel industrial efficacy.
FAQ
What are the main types of hydraulic pumps?
Gear, vane, and piston pumps. Each type has unique features suited for different pressure and efficiency requirements.
How does operational pressure influence pump selection?
A pump must handle the system’s maximum pressure to avoid failure. Higher pressures often require sturdier materials and elevate costs.
Why is flow rate important for pump efficiency?
Optimal flow ensures responsive operation without waste. Deviations lead to delays or excess energy use.
What role does fluid compatibility play in pump performance?
Matched fluids prevent corrosion and maintain lubrication, extending life and upholding efficiency.
How does pump size and speed affect performance?
Size influences volume per cycle, while speed scales output; mismatches raise wear or power demands.
What impact do temperature and viscosity have on a hydraulic pump? Deviations from ideals increase friction or slippage, demanding more power and risking damage.
Why is choosing the right manufacturer important?
Reliable manufacturers deliver certified quality and adaptable solutions for diverse needs.
Partner with POOCCA: Elevate Your Operations with Trusted Hydraulic Pump Manufacturers and Suppliers
For industrial entities seeking durable, high-performance hydraulic pumps, partnering with a dedicated factory like POOCCA unlocks unparalleled value. As a premier manufacturer and supplier, POOCCA integrates over 20 years of expertise in R&D, production, and customization to deliver gear, vane, and piston pumps that meet rigorous demands. With more than 1,600 models certified to ISO, CE, and ROHS standards, POOCCA ensures seamless compatibility for construction, agriculture, and manufacturing applications.
Bulk orders benefit from competitive factory pricing, rapid 5-7 day delivery, and 12-month warranties backed by global support. Contact POOCCA today at sales@kamchau.com or +86 18927498997 to discuss tailored solutions and streamline your supply chain.