Two common pump types are gear pumps and piston pumps, each with special features. This blog explores the difference between gear pump and piston pump to help you choose the best one for your needs.

What Are Hydraulic Gear Pumps and Piston Pumps?
To grasp the difference between gear pump and piston pump, let’s first examine what each pump does.
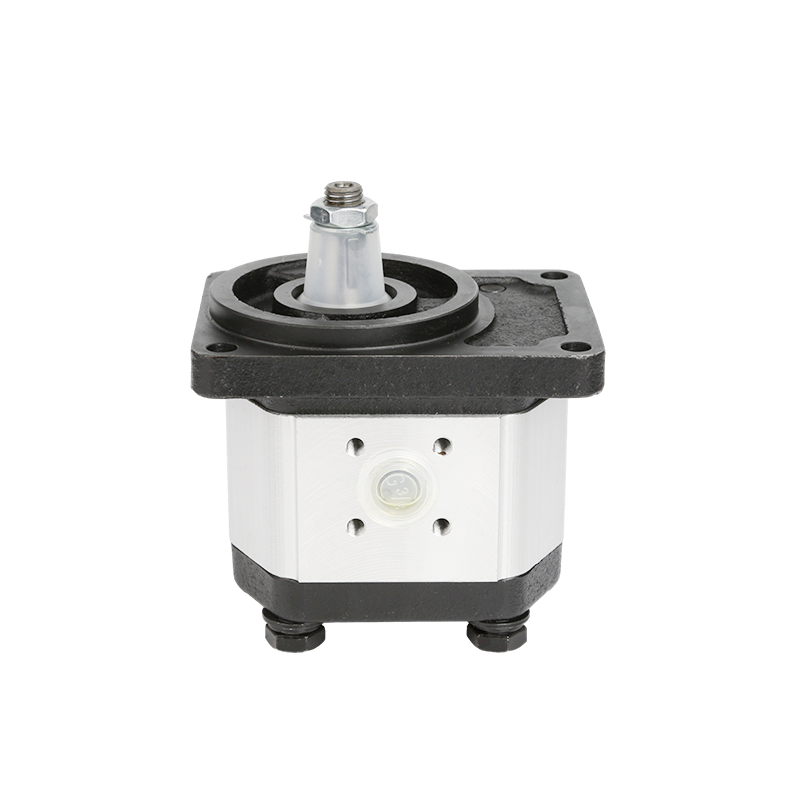
What Are Gear Pumps

Gear pumps are basic devices that use spinning gears to move hydraulic fluid. They are positive displacement pumps. This means they shift a set amount of fluid with each turn. Their design makes them great for low-pressure jobs where steady flow is required.
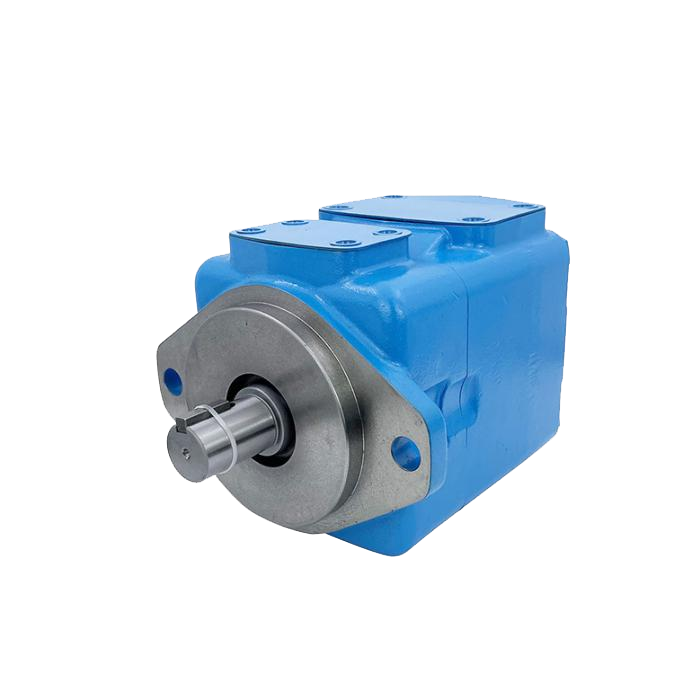
What Are Piston Pumps

In contrast, piston pumps use pistons that slide back and forth to push fluid. They can be fixed or variable displacement. This makes them perfect for high-pressure tasks where flow must adjust.
Understanding the hydraulic gear pump vs. piston pump difference helps you select the right pump for your system.
Key Differences Between Gear Pump and Piston Pump
When you compare gear pump and piston pump, several factors stand out.
- Mechanism: Gear pumps use rotating gears. Piston pumps use moving pistons.
- Displacement: Gear pumps usually have fixed displacement. Piston pumps often allow variable displacement.
- Pressure Range: Gear pumps manage up to ~4,500 PSI. Piston pumps handle up to ~14,500 PSI.
- Flow Characteristics: Gear pumps give steady flow. Piston pumps adjust to needs.
Design and Working Principles
Design and Working Principle of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps have a simple design. This is a key point when you compare gear pump and piston pump. They use two meshing gears, either internal or external. The gears spin to create suction. As they turn, they capture fluid and push it through an outlet. This fixed displacement design means gear pumps deliver a constant amount of fluid per spin. To change flow, you need extra valves. This adds some complexity to the system.
The basic design of gear pumps has fewer moving parts. This makes them strong and easy to fix. They shine in industries like food processing or chemical plants. There, thick fluids need steady movement. For example, gear pumps move syrups in food production or oils in chemical factories. Their dependability in low-pressure tasks makes gear pump and piston pump comparisons favor gear pumps for budget-friendly uses.
Gear pumps are simple devices. They use spinning gears to move hydraulic fluid. The gears, either internal or external, mesh together. As they turn, they pull in fluid and push it out. This creates a steady flow. The design is basic with fewer parts. This makes gear pumps strong and easy to maintain. They work well for low-pressure tasks.
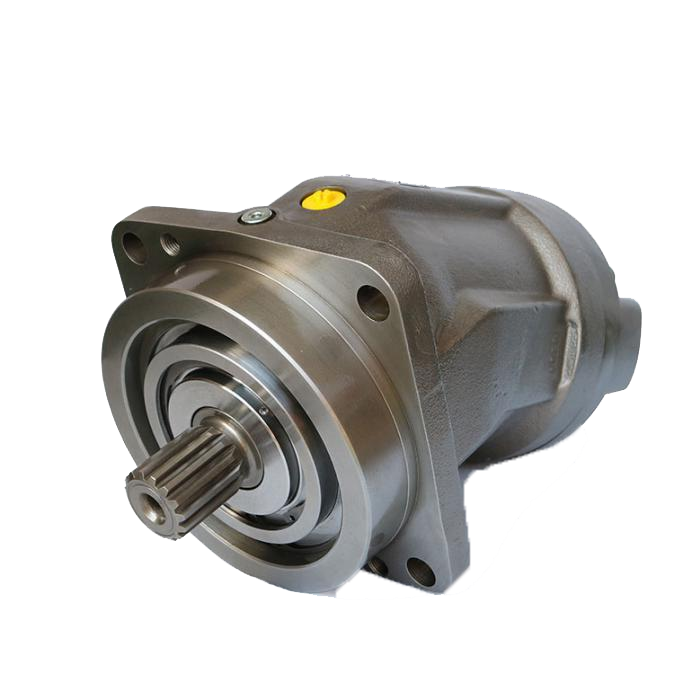
Design and Working Principle of Piston Pumps
Piston pumps are more complicated. This is a vital factor in the difference between gear pump and piston pump. They use pistons that slide in cylinders. A swash plate or cam drives them. This motion pressurizes fluid and moves it through the pump. A big advantage is variable displacement. By adjusting the swash plate angle, you change the flow rate. This makes piston pumps flexible for systems with changing needs.
There are two main types: axial piston pumps and radial piston pumps. In axial pumps, pistons align parallel to the shaft. In radial pumps, pistons are arranged around the shaft. Axial designs are more common for high-pressure jobs, like powering excavators or industrial presses. The ability to adjust flow makes piston pump vs. gear pump comparisons highlight piston pumps for active, high-pressure systems. For example, construction equipment uses piston pumps for precise control under heavy loads.
Performance Comparison: Gear Pump vs. Piston Pump
Pressure Capabilities
- Gear Pumps:
They work at pressures of 3,000–4,500 PSI. They are suitable for low-to-medium pressure jobs. - Piston Pumps:
They handle pressures up to 14,500 PSI. They are ideal for high-pressure tasks, like heavy machinery or industrial presses.
Flow Characteristics
- Gear Pumps:
They deliver steady, even flow. They are great for stable systems. But they can be wasteful in changing systems. They cannot adjust output without extra valves. This limits efficiency in systems with varying needs. - Piston Pumps:
Variable displacement models adjust flow to match system needs. They save energy in active systems by reducing unneeded flow.
Efficiency and Energy Savings
- Gear Pumps:
Fixed displacement delivers constant flow, no matter the need. This can waste energy in systems with changing flow demands, like mobile machinery. For example, they use full power even during light tasks. This increases fuel costs. - Piston Pumps:
Variable displacement adjusts flow to system needs. This reduces energy waste. They are more efficient in fast or varying-load systems, like construction equipment. They use less fuel and lower operating costs. This provides better long-term savings.
Noise and Vibration Levels
- Gear Pumps:
They run smoothly at lower speeds. They produce less noise and vibration. The simple gear mechanism ensures steady motion. They are ideal for quiet environments, like food processing plants. - Piston Pumps:
Axial designs are noisier because of complex piston movement. Vibrations can be an issue in tight spaces. Radial piston pumps and modern electronic controls reduce noise. They manage flow precisely. Advanced controls help piston pumps become almost as quiet as gear pumps.
Applications of Gear Pumps and Piston Pumps
The applications of gear pump vs. piston pump show their strengths.
Gear Pump Applications in Detail
Gear pumps perform well in tasks needing steady flow at lower pressures. In food processing, they move syrups, oils, or other thick liquids accurately. In chemical manufacturing, they handle fluids like lubricants or paints. These fluids are often thick. Their simple design makes them reliable for steady tasks, like lubrication systems in machinery. However, when you compare gear pump and piston pump, gear pumps are less suited for high-pressure or changing-flow systems. They need extra valves to adjust flow. This can add complexity.
Piston Pump Applications in Detail
Piston pumps are the top choice for high-pressure and active systems. In construction, they power hydraulic cylinders in excavators and bulldozers. They handle heavy loads easily. In industrial settings, piston pumps drive presses or injection molding machines. Precise control is crucial there. Aerospace systems also use piston pumps. They manage high pressures and adapt to changing needs. The difference between gear pump and piston pump in applications shows piston pumps are better for heavy-duty tasks. But their complexity means higher costs and maintenance.
How to Choose Between Gear Pump and Piston Pump

Choosing the right pump depends on your system’s needs. First, check pressure requirements. If your task needs pressures above 4,500 PSI, like in heavy machinery, piston pumps are better. For low-to-medium pressure tasks, like fluid transfer in manufacturing, gear pumps work well. Next, think about flow control. Piston pumps adjust flow dynamically. They are ideal for systems with changing needs. Gear pumps suit steady flow needs.
Budget is another factor. Gear pumps cost less upfront. But piston pumps save money over time due to efficiency. Finally, consider noise and space. Gear pumps are quieter and smaller. Piston pumps may need noise-reducing controls.
Why Choose POOCCA for Gear Pump and Piston Pump Solutions?
POOCCA has over 20 years of experience in designing and making hydraulic pumps. Their gear pump and piston pump customization services meet specific industry needs. They ensure top performance. With exports to over 120 countries, POOCCA is trusted for dependability and quality. Their 12-month guarantee and technical support provide confidence. Ready to improve your hydraulic system? Visit https://www.kamchau.com/ or contact now to explore POOCCA’s gear pump and piston pump solutions designed for you.