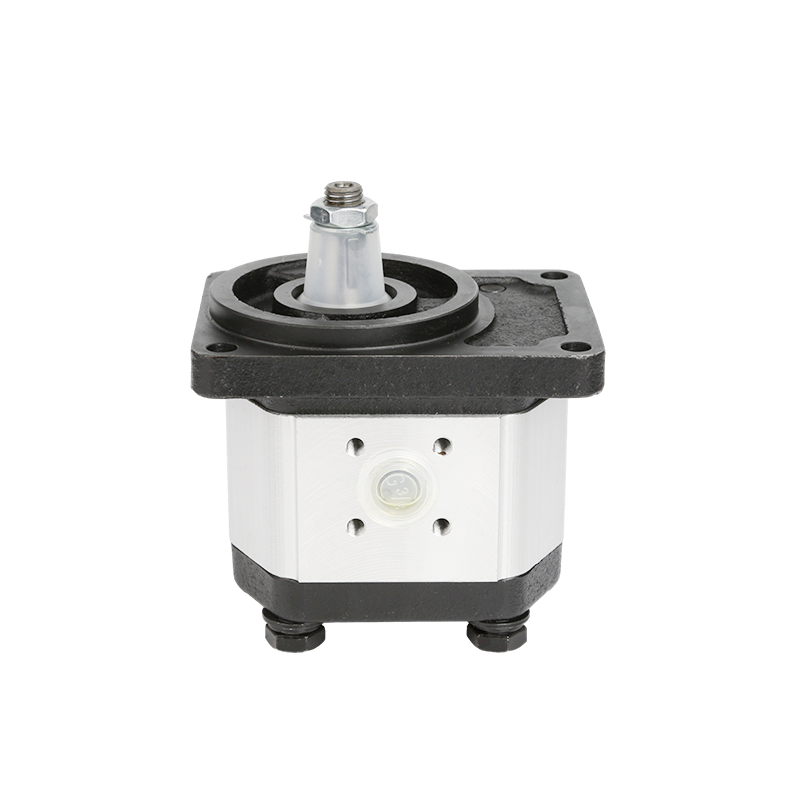
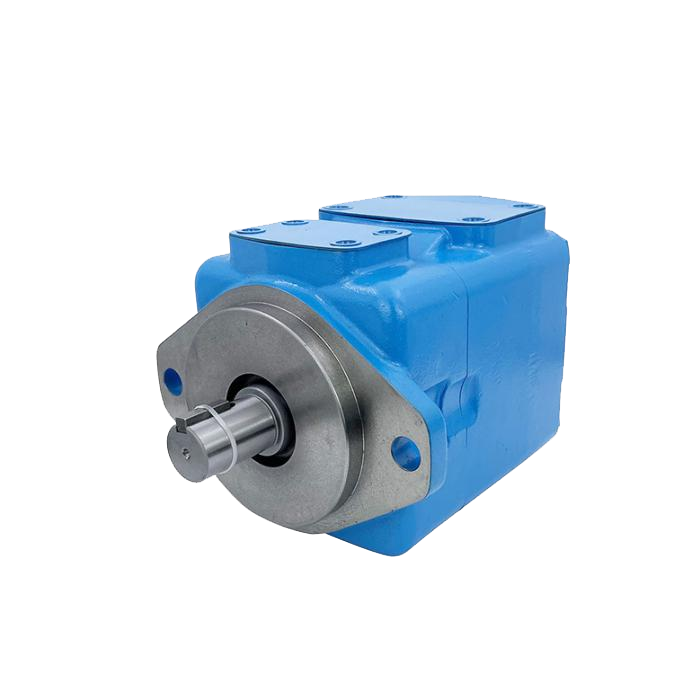
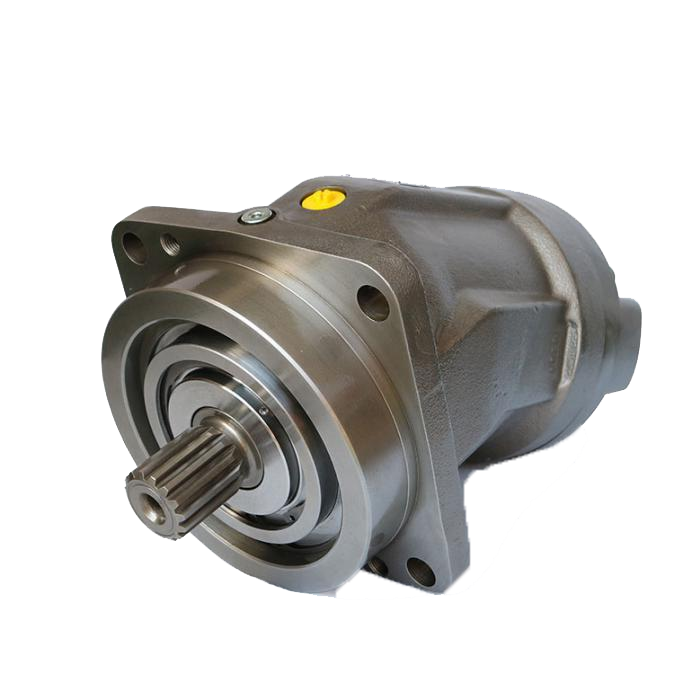
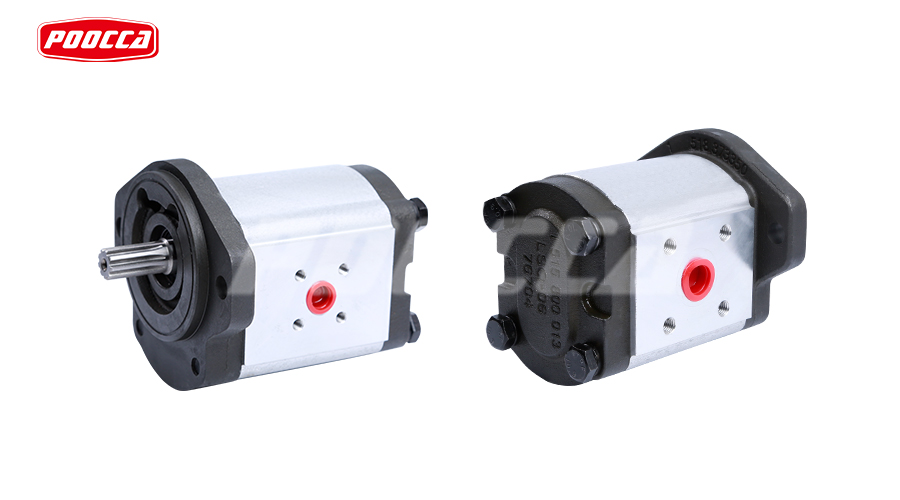
Understanding Gear Pumps and Their Importance
Gear pumps play a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in hydraulic systems. Gear pumps are positive displacement pumps that transfer fluids using the meshing of gears to create suction and discharge action. These pumps are widely used due to their compact structure, low noise, and efficient fluid transfer capabilities.
What Are Gear Pumps?
The Basics of Gear Type Pump Operation
The operation of gear type pumps is based on the interlocking of two gears, the driver gear, and the driven gear. As the gears rotate, they create a vacuum at the pump inlet, allowing fluid to enter the pump. The fluid is then carried between the gear teeth and the casing to the outlet side of the pump.
Hydraulic Gear Pump: A Closer Look
In hydraulic gear pumps, mechanical energy is converted into hydraulic energy within a fluid. This conversion process makes them essential components in hydraulic systems used across various industries.
The Role of Gear Pumps in Hydraulic Systems
Applications and Significance
The demand for gear pumps is closely linked to key industries such as oil & gas, chemicals, automotive, and agriculture. According to market analysis reports, the global hydraulic gear pump market is anticipated to expand significantly in the coming years. The thriving oil & gas and chemical industries are driving this growth, with Asia-Pacific leading the market due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
The compact structure and high energy density of gear pumps make them suitable for power systems, steering systems, transmission systems, manufacturing processes, and other applications requiring precise fluid flow control.
Statistical Data:
- The Global Hydraulic Gear Pump Market is anticipated to expand in the coming years.
- The gear pump market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.88% during the forecast period.
- The need for gear pumps has surged as a result of strong industrial growth in nations like China, India, Japan, South Korea, and others.
Scientific Research Findings:
- Ongoing advancements in gear pump technology enhance performance and reliability.
- Internal gear pumps are lauded for their ability to handle diverse fluids with precision.
By understanding these fundamental aspects of gear pumps, it becomes evident why they are integral components in hydraulic systems across various industries.
Common Faults in Gear Pumps and Their Causes
Gear pumps are known for their reliability and efficiency, but like any mechanical system, they are susceptible to faults. Understanding the symptoms and root causes of gear pump failure is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in hydraulic systems.
Identifying Symptoms of Gear Pump Failure
When a gear pump begins to fail, it exhibits certain symptoms that indicate underlying issues. Noise, vibration, and efficiency loss are common indicators of potential gear pump problems. Unusual noises such as grinding, whining, or knocking may suggest internal components are wearing out or becoming misaligned. Excessive vibration can point to imbalanced gears or worn bearings. Additionally, a decrease in efficiency, noticeable through reduced fluid flow or pressure output, signals potential issues within the pump.
Analyzing the Root Causes
Insufficient NPSHa and Air Leaks
One of the primary causes of gear pump failure is insufficient Net Positive Suction Head available (NPSHa). This occurs when the pressure at the suction side of the pump falls below the vapor pressure of the liquid being pumped, leading to cavitation. Cavitation can cause erosion of the gear teeth and housing, ultimately compromising the pump’s performance.
Air leaks within the system also contribute to gear pump malfunctions. When air infiltrates the hydraulic fluid, it creates air pockets that disrupt smooth fluid flow and increase system pressure. This can lead to decreased volumetric efficiency and potential damage to internal components.
High Temperatures and Sudden Shock Loads
Elevated temperatures pose a significant threat to gear pumps as they can accelerate wear on critical components such as gears, bearings, and seals. Overheating may result from excessive friction due to inadequate lubrication or prolonged operation under heavy loads.
Sudden shock loads produced by abrupt over-pressurization of the hydraulic system may cause immediate failure of the pump drive shaft or other internal components. These shock loads place immense stress on the gears and bearings, potentially leading to catastrophic failure if not addressed promptly.
The above-mentioned symptoms and root causes shed light on why proactive maintenance and troubleshooting strategies are essential for ensuring long-term reliability in gear pumps.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Troubleshooting Gear Pumps
When troubleshooting gear pumps, a systematic approach is essential to identify and address common faults effectively. By following step-by-step solutions, maintenance professionals can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of gear pumps in hydraulic systems.
Initial Inspection and Seal Check
The initial inspection serves as the foundation for identifying potential issues within the gear pump. A thorough examination should focus on addressing leakage and seal wear, which are common culprits behind pump inefficiency.
During the inspection, it’s crucial to check for any visible signs of leakage around the pump housing, connections, and fittings. Additionally, inspecting the seals for wear or damage is imperative to prevent fluid loss and maintain proper pressure levels within the system.
Corrective Actions for Common Faults
Adjusting Suction Pressure and Verifying Rotation Direction
Adjusting suction pressure is a fundamental corrective measure to optimize gear pump performance. By ensuring that the suction pressure meets the manufacturer’s specifications, cavitation risks can be minimized, promoting smooth fluid flow and preventing premature wear on internal components.
Verifying rotation direction is equally important in troubleshooting gear pumps. Incorrect rotation direction can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage to gears and bearings. This can be rectified by carefully adjusting the motor or drive unit to ensure proper rotation alignment.
Gasket, Seal, and Impeller Maintenance
Regular maintenance of gaskets, seals, and impellers is vital for preventing potential failures in gear pumps. Inspecting these components for wear, cracks, or degradation allows for timely replacements or repairs as needed.
Gaskets play a critical role in preventing fluid leakage between mating surfaces. Regularly checking gaskets for compression set or deterioration ensures a reliable seal that minimizes the risk of leaks.
Seals are another integral part of gear pumps that require routine maintenance. Monitoring seal condition and addressing any signs of wear or damage prevents fluid bypass and maintains optimal pressure levels within the system.
Impeller maintenance involves inspecting the impeller blades for erosion or corrosion that may affect fluid transfer efficiency. Cleaning impeller surfaces and ensuring proper alignment with casing components contribute to sustained pump performance.
By implementing these step-by-step solutions for troubleshooting gear pumps, maintenance professionals can effectively address common faults while promoting long-term reliability in hydraulic systems.
Choosing the Right Gear Pump: Advice from Gear Pump Suppliers
When selecting a gear pump for a specific application, it is essential to consider various factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Gear pumps are available in different types, sizes, and operational specifications, and understanding these considerations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gear Pump
Type, Size, and Operational Requirements
The first consideration when choosing a gear pump is the type, which includes internal gear pumps, external gear pumps, and gerotor pumps. Each type has distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. Internal gear pumps are known for their precise fluid handling capabilities, while external gear pumps excel in high-pressure applications. Gerotor pumps are valued for their compact size and minimal pulsation output.
Next, size plays a critical role in determining the flow rate and pressure capacity of the gear pump. It is important to match the pump size with the system requirements to ensure optimal fluid transfer without overloading or underutilizing the pump.
Operational requirements such as speed variations, temperature ranges, and fluid compatibility also influence the selection of a gear pump. Understanding these operational parameters helps in identifying a pump that can withstand the demands of the intended application.
POOCCA hydraulic manufacturer gear pumps include internal gear pumps and external gear pumps. Our main markets for hydraulic gear pumps are in Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Philippines, Russia, etc. Indeed, POOCCA has more than 30 years of experience in the production, manufacturing and maintenance of hydraulic gear pumps. With industry experience, POOCCA has built a strong reputation for excellence and reliability. The company’s commitment to innovation, quality, sustainability and customer satisfaction has earned it the trust and loyalty of customers around the world.
Final Thoughts and Preventative Measures
As gear pumps are vital components in hydraulic systems, implementing regular maintenance practices is essential to ensure their longevity and optimal performance. By adopting preventative measures, industry professionals can mitigate potential faults and extend the useful life of gear pumps.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Scheduled inspections and early detection play a pivotal role in maintaining the health of gear pumps. Conducting routine assessments allows for the identification of wear, damage, or potential issues before they escalate into critical failures. This proactive approach enables maintenance teams to address concerns promptly, minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs.
Survey Results:
- According to a survey focused on predicting the remaining useful life of gear pumps, 85% of respondents emphasized the significance of scheduled inspections for early fault detection.
- The methodology for predicting remaining useful life highlighted that regular maintenance practices contribute significantly to extending the operational lifespan of gear pumps.
Adopting Best Practices for Gear Pump Longevity
Temperature control is a crucial aspect of ensuring gear pump longevity. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures prevents excessive thermal stress on internal components, preserving their integrity and functionality over time. Additionally, avoiding over-pressurization safeguards against sudden shock loads that can compromise the structural integrity of gear pumps.
Key Statistics:
- The methodology for predicting remaining useful life of gear pumps underscored temperature control as a key factor in prolonging pump lifespan.
- Respondent demographics focused on gear pumps commonly used in the hydraulic field highlighted temperature regulation as a prevalent best practice among industry professionals.
By prioritizing regular maintenance and adhering to best practices such as temperature control and pressure management, businesses can optimize the reliability and efficiency of gear pumps within their hydraulic systems.
In conclusion, proactive maintenance strategies coupled with adherence to best practices are instrumental in maximizing the operational lifespan of gear pumps. As industries continue to rely on these essential components, investing in preventative measures is paramount for sustained performance and cost-effective operations.